Golang数据类型&内置函数深入学习-Golang夯实基础第一天
-
数据类型
-
值类型
类型 名称 具体类型 bool 布尔型 boolint 整型 intint8int16int32int64uint 无符号整型 uintuint8uint16uint32uint64float 浮点型 float32float64string 字符串 stringcomplex 复合型 complex64complex128array 数组 [长度]数据类型uintptr 指针地址 uintptrstruct 结构体 type xxx struct{}func TestValueType(t *testing.T) { //bool var b1, b2 bool = true, false //int 看系统是32位的还是64位的,长度和系统相等 //32位系统->int32 var a int = 1 // int8 int16 int32 int64 var ( a1 int8 = 9 a2 int16 = 8 a3 int32 = 7 a4 int64 = 6 ) //uint 无符号整数 看系统是32位的还是64位的,长度和系统相等 //32位系统->uint32 var u uint = 11 // uint8 uint16 uint32 uint64 var ( u1 uint8 = 99 u2 uint16 = 98 u3 uint32 = 97 u4 uint64 = 96 ) // float32 float64 浮点型 var ( f1 float32 = 1.1 f2 float32 = 2.2 ) // string 字符串类型 // 字符串类型是所有8位字符的集合 // ,字符串可以为空,但是不能位nil, // 字符串类型的值是不可变的, // 每一次的赋值都是重新生成 var ( s1 string = "Hello Go!" s2 string = string([]byte{'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ' ', 'G', 'o', '!'}) ) //complex64 complex128 复数,需要相关数学知识,且开发很少使用,仅了解 var ( cp1 complex64 = 1 + 5i cp2 complex64 = complex(1, 5) cp3 complex128 = 8 + 5i cp4 complex128 = complex(8, 5) ) //array 【固定】长度数组 核心:固定 var ( arr1 [3]int = [3]int{7, 8, 9} arr2 [2]string = [2]string{"hello", "Go"} ) // uintptr 这是一个特殊的无符号整数型,它足够大,确保能够存下任何指针的地址值 var uptr uintptr = uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(&a)) //struct 结构体类型 golang中没有class关键字来定义类,但是可以将struct变量看作一个类的实例 // 在每次赋值的时候,struct也属于值传递 type Student struct { Name string Age int } stu := Student{"xxcheng", 18} stu2 := stu stu.Name = "jpc" fmt.Println( "-------------", "\n", b1, b2, "\n", a, a1, a2, a3, a4, "\n", u, u1, u2, u3, u4, "\n", f1, f2, "\n", s1, s2, "\n", cp1, cp2, cp3, cp4, "\n", arr1, arr2, "\n", uptr, "\n", stu, stu2, "\n", "-------------", ) }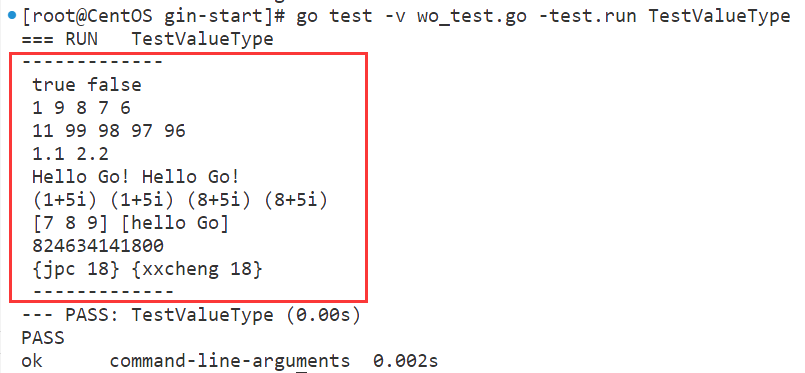
各数据类型默认零值测试
func TestDefaultZero(t *testing.T) { var ( a int b float32 c complex64 d string e1 [3]int e2 [3]string f uintptr ) fmt.Println(a, b, c, d, e1, e2, f) }
-
引用类型(指针类型)
类型 名称 格式 slice 切片 []数据类型 map 键值对 map[key数据类型]value数据类型 chan 通道 chan 数据类型 func TestReferenceType(t *testing.T) { // slice 切片类型 长度不固定的数组 var s1 []int = []int{9, 8, 5} var s2 []int = make([]int, 4) s2[2] = 666 // map 键值对 // 最后一条键值对也要添加逗号 var m1 map[string]int = map[string]int{ "age": 18, "sex": 0, } var m2 map[string]string = make(map[string]string, 3) m2["age"] = "xxcheng" // chan 通道 用于通信使用,分为无缓存和有缓存 // 无缓存 var c1 chan int = make(chan int) // 有缓存 var c2 chan string = make(chan string, 2048) go func() { for i := 0; i < 3; i++ { fmt.Println("【无缓存】发送端:", i*10) c1 <- i * 10 } }() go func() { for i := 0; i < 3; i++ { fmt.Println("【有缓存】发送端:现在是:", i) c2 <- fmt.Sprintf("现在是:%d", i) } }() go func() { for i := 0; i < 3; i++ { fmt.Println("【无缓存】接收端:", <-c1) } }() go func() { for i := 0; i < 3; i++ { fmt.Println("【有缓存】接收端:", <-c2) } }() fmt.Println( "---------------", "\n", s1, s2, "\n", m1, m2, "\n", "---------------", ) for { } }
证明
interface类型是引用类型func (m *Man) Say() { fmt.Println("name:", m.Name, ",age:", m.age) } func TestOther(t *testing.T) { var man Man = Man{"xxcheng", 18} var man2 Man = man var person Person = &man man.Name = "jpc" man2.Say() person.Say() }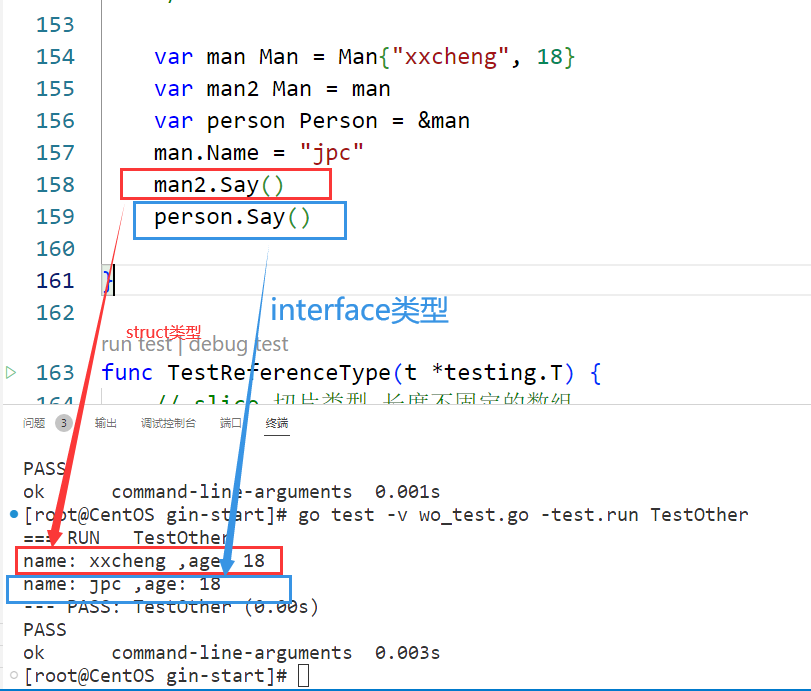
-
拓展
- 值类型和引用类型两者之间的主要区别:拷贝操作和函数传参。
-
-
内置函数
-
append添加n个元素到切片的末尾
func append(slice []Type, elems ...Type) []Typefunc TestBuildinFuncAppend(t *testing.T) { a := []int{7, 8, 9} b := append(a, 999) c := []int{11, 22, 33} d := append(a, c...) fmt.Println(b, d) }
-
cap返回变量占用的实际容量
func cap(v Type) intArray: the number of elements in v (same as len(v)). Pointer to array: the number of elements in *v (same as len(v)). Slice: the maximum length the slice can reach when resliced; if v is nil, cap(v) is zero. Channel: the channel buffer capacity, in units of elements; if v is nil, cap(v) is zero.func TestBuildinFuncCap(t *testing.T) { arr := [3]int{7, 8, 9} arr[0] = 111 slice := make([]int, 4) slice = []int{1, 2, 3, 4} slice = append(slice, 88) slice2 := []int{} fmt.Println( "----"+"\n", "arr:", cap(arr), "\n", "&arr:", cap(&arr), "\n", "slice:", cap(slice), "\n", "slice2:", cap(slice2), ) }
-
close关闭通道
func TestBuildinFuncClose(t *testing.T) { defer fmt.Println("bye~~~") c := make(chan int, 4) go func() { defer fmt.Println("exit send") for i := 111; i < 9999; i++ { c <- i if i == 119 { close(c) break } } }() go func() { defer fmt.Println("exit receive") for { v, ok := <-c if !ok { break } fmt.Println("receive:", v) } }() time.Sleep(time.Second * 5) }
-
complex返回一个复数
func complex(r, i FloatType) ComplexTypefunc TestBuildinFuncComplex(t *testing.T) { c := complex(2.2, 3.3) fmt.Println(c) }
-
copy复制一个切片的数据到另外一个切片
特殊情况,可以将一个字符串复制到一个byte切片
返回一个int类型,表示成功复制了多少个
func copy(dst, src []Type) intfunc TestBuildinFuncCopy(t *testing.T) { a := []int{1, 2, 3} // 这里特别注意,切片需要初始化分配空间,否则copy不进去数据的 var b []int = make([]int, 3) c := "ABC" var d []byte = make([]byte, 3) var e []byte = make([]byte, 2) // 这里不初始化分配空间,进行测试 var f []byte l1 := copy(b, a) l2 := copy(d, c) l3 := copy(e, c) l4 := copy(f, c) fmt.Println(a, c) fmt.Println(b, d, e, f) fmt.Println(l1, l2, l3, l4) }
-
delete删除指定键值对的key元素
func delete(m map[Type]Type1, key Type)func TestBuildinFuncDelete(t *testing.T) { m := map[string]string{ "name": "xxcheng", "sex": "男", } fmt.Println(m) delete(m, "name") delete(m, "age") fmt.Println("----------") fmt.Println(m) }
-
imag给定一个复数,返回其虚部
func imag(c ComplexType) FloatTypefunc TestBuildinFuncImag(t *testing.T) { c := 3.3 + 5.5i i := imag(c) fmt.Println(i) }
-
len根据数据类型返回对应规则下的长度,并非实际容量长度,一般与
cap配合使用func len(v Type) intArray: the number of elements in v. Pointer to array: the number of elements in *v (even if v is nil). Slice, or map: the number of elements in v; if v is nil, len(v) is zero. String: the number of bytes in v. Channel: the number of elements queued (unread) in the channel buffer; if v is nil, len(v) is zero.func TestBuildinFuncLen(t *testing.T) { arr := [3]int{7, 8} arr2 := [0]int{} slice := make([]int, 8) str := "ABC" c := make(chan int) c2 := make(chan int, 4) go func() { for { c <- 333 } }() go func() { for { c2 <- 333 } }() time.Sleep(time.Second * 3) fmt.Println( "-------", "\n", "arr:", len(arr), "\n", "&arr:", len(&arr), "\n", "arr2:", len(arr2), "\n", "&arr2:", len(&arr2), "\n", "&slice:", len(slice), "\n", "&str:", len(str), "\n", "&c:", len(c), "\n", "&c2:", len(c2), "\n", "-------", ) }
-
make初始化和分配内存,只能用于
slice、map和chan类型func make(t Type, size ...IntegerType) TypeSlice: The size specifies the length. The capacity of the slice is equal to its length. A second integer argument may be provided to specify a different capacity; it must be no smaller than the length. For example, make([]int, 0, 10) allocates an underlying array of size 10 and returns a slice of length 0 and capacity 10 that is backed by this underlying array. Map: An empty map is allocated with enough space to hold the specified number of elements. The size may be omitted, in which case a small starting size is allocated. Channel: The channel's buffer is initialized with the specified buffer capacity. If zero, or the size is omitted, the channel is unbuffered.func TestBuildinFuncMake(t *testing.T) { slice := make([]int, 3) slice2 := make([]int, 0, 3) fmt.Println(len(slice), len(slice2)) fmt.Println(slice, slice2) fmt.Println("------") m1 := make(map[string]int) m2 := make(map[string]int, 3) fmt.Println(len(m1), m1) fmt.Println(len(m2), m2) fmt.Println("------") c1 := make(chan int) c2 := make(chan int, 3) fmt.Println(len(c1), c1) fmt.Println(len(c2), c2) }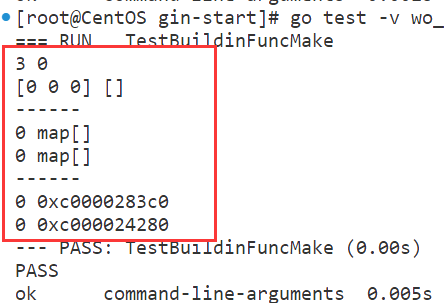
-
new返回一个初始化一个指定类型的函数并且分配好内存的变量的指针
func new(Type) *Typefunc TestBuildinFuncNew(t *testing.T) { a := new(int) fmt.Printf("%T,%v\n", a, *a) arr := new([3]int) fmt.Printf("%T,%v\n", arr, arr) slice := new([]int) fmt.Printf("%T,%v", slice, slice) }
make与new的异同点- 相同点:
- 都是在堆上分配内存;
- 不同点
make返回的是对应的传入的数据类型,new返回的是对应的传入的数据类型的指针;make只能使用在slice、map和chan的创建
- 相同点:
-
panic抛出一个异常
在此之后代码不会执行,但是会先调用在此之前声明了的
defer,然后返回调用当前函数的函数,调用当前函数的函数之后的代码也不会执行,但是会先调用在此之前声明了的defer,依次执行最后结果执行,除非当异常被捕获,才能正常执行官方原文
The panic built-in function stops normal execution of the current goroutine. When a function F calls panic, normal execution of F stops immediately. Any functions whose execution was deferred by F are run in the usual way, and then F returns to its caller. To the caller G, the invocation of F then behaves like a call to panic, terminating G's execution and running any deferred functions. This continues until all functions in the executing goroutine have stopped, in reverse order. At that point, the program is terminated with a non-zero exit code. This termination sequence is called panicking and can be controlled by the built-in function recover.
func panic(v any)func HandlePanic_A() { defer fmt.Println("HandlePanic_A defer") fmt.Println("HandlePanic_A func") HandlePanic_B() fmt.Println("HandlePanic_A2 func") } func HandlePanic_B() { defer fmt.Println("HandlePanic_B defer") fmt.Println("HandlePanic_B func") HandlePanic_IN() fmt.Println("HandlePanic_B2 func") } func HandlePanic_IN() { defer fmt.Println("HandlePanic_IN defer") fmt.Println("HandlePanic_IN func") panic("呃呃呃呃") fmt.Println("HandlePanic_IN_2 func") } func TestBuildinFuncPanic(t *testing.T) { HandlePanic_A() }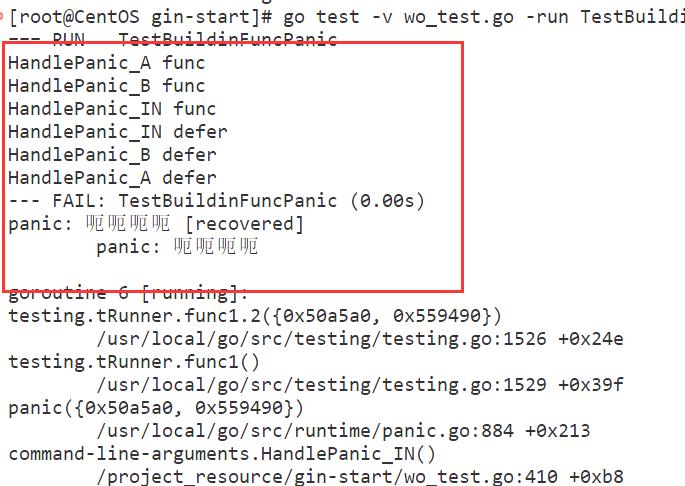
-
print见
printlnfunc print(args ...Type) -
println将内容按照指定格式的形式输出到标准错误流,而
fmt包是将内容输出到标准输出流,一般是屏幕输出,根据官方的说明,不是很推荐使用,并且有可能会在之后的版本被抛弃,并且输出内容和格式也和fmt很不一样func println(args ...Type)func TestBuildinFuncPrint(t *testing.T) { a := 5 b := []int{4, 5, 6} println(a, b) print(a, b) fmt.Println() fmt.Println(a, b) fmt.Print(a, b) }
-
real给定一个复数,返回其实部
func real(c ComplexType) FloatTypefunc TestBuildinFuncReal(t *testing.T) { c := 3.3 + 5.5i i := real(c) fmt.Println(i) }
-
recover捕获
panic,使程序恢复正常,recover只有在defer的函数里面才能发挥真正的作用func recover() anyfunc makeError() { fmt.Println("我是makeError Top") panic("我是makeError 我丢一个错误") fmt.Println("我是makeError Bottom") } func catchError() { defer func() { if r := recover(); r != nil { fmt.Println("我是catchError 捕获到一个Error ", r) } }() fmt.Println("catchError Top") makeError() fmt.Println("catchError Bottom") } func TestBuildinFuncRecover(t *testing.T) { fmt.Println("TestBuildinFuncRecover Top") catchError() fmt.Println("TestBuildinFuncRecover Bottom") }
-
-
参考链接
本作品采用 知识共享署名-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议 进行许可。
 小小程日记-笔记分享
小小程日记-笔记分享
tql 不愧是黑哥
雪豹闭嘴
太厉害了吧!
欢迎大佬~